Skinny to Muscular
How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries: Essential Tips
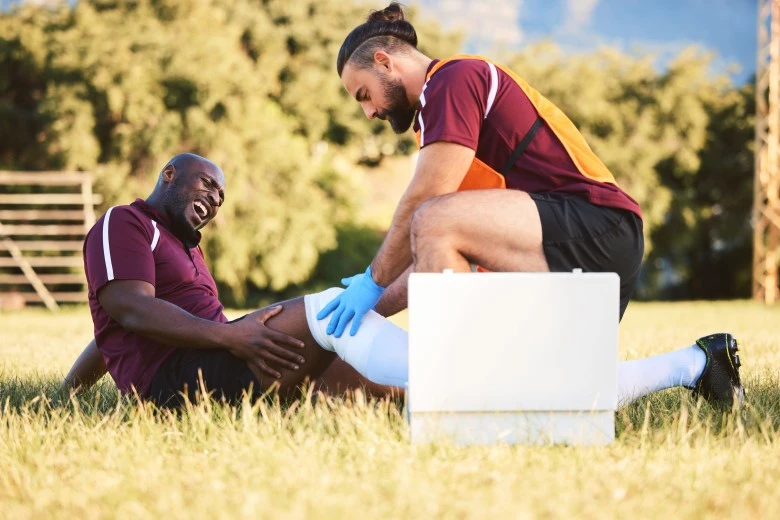

Want to know about how to prevent hamstring injuries? Hamstring injuries are common among sports, exercisers, and athletes and cause pain. With the correct knowledge, preventive exercises, and recovery strategies to help build stronger and more resilient hamstrings. In this article, we will cover hamstring anatomy, what is a hamstring injury, grades of hamstrings, do hamstring, how to prevent hamstring injuries, top 5 exercises, advanced exercises with issues and benefits, and much more.
Let’s get to it!
Hamstrings Anatomy:
They are skeletal muscles. They are three in number and used by our bodies for work, climbing stairs, squats, and performing many other leg movements.
It comes from the English word Hamm, a group of three muscles.
What Is Hamstring Injury: How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries
In muscles and tendons, group hamstring injury is a strain in the back of the thigh. It is one of the common injuries in athletes and exercise beginners.
Grades Of Hamstring Injury: How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries:
Rest and recovery should be noticed when learning how to prevent hamstring injuries. The grade excellently describes the severity of the hamstring injury:
- Grade 1: A mild muscle pull strain.
- Grade 2: A partial muscular tear.
- Grade 3: A complete muscle tear.
Do Hamstring Injuries Hurt: How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries
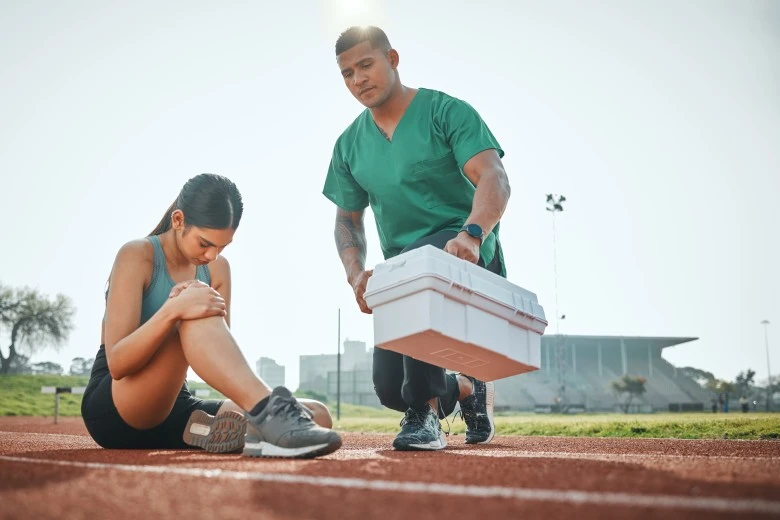

Yes, the pain in my thigh comes on suddenly. Follow the RICE procedure. Understanding how to prevent hamstring injuries is like installing a safety net in a tightrope walker.
Reasons For Getting Hamstring Injuries:
Hamstring injuries occur in a lot of ways. Some reasons include
- Ineducately warming up
- Ineducately preconditioning program
- Previous hamstring injury
- Fatigue from training to hard
- A direct blow to two thigh
These are some reasons physical therapists often guide patients on how to prevent hamstring injuries through targeted training.
Symptoms Of Hamstring Injury: How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries
Grade One: Strain: Sudden radiating pain in the back of the thigh. Although strength will not be affected, it will be hard to move leg.
Grade 2: Partial Tear: This is more painful than Grade One. The patient has some swelling and loss of strength in both legs.
Grade 3: Severe Tear: Rose pain tenderness, swelling, and brushing. The patient might feel a popping sensation with the injury.
Other Symptoms Include:
- Spasms
- bump or not in the thigh area
- Muscle stiffness is especially apparent after cooling down.
Top 5 Exercises In How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries:
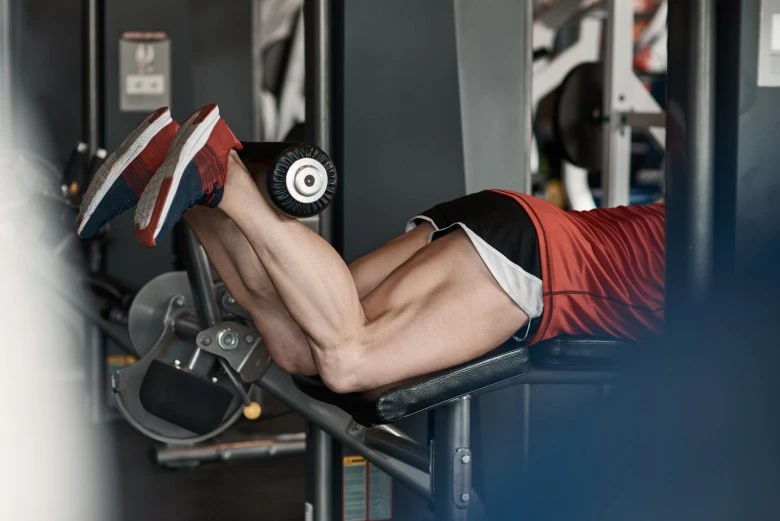

How to prevent hamstring injuries? It is like laying a foundation before building a skyscraper, but it is also essential for long-term success. Their top 5 exercises are as follows:
| Exercise | Key Focus Area | Helping in How to Prevent Hamstring Injuries | Repetition and Frequency |
| Isometric hamstring of flux | Hamstrings stability | Strengthening hamstrings reduces the risk of strain by enhancing stability. | 10 to 15 reps three times per week. |
| Nordic hamstring exercise | Eccentric strength | Focuses on eccentric contracting, crucial to prevent hamstring strange during sudden movement | 8 to 10 reps, 2 times per week |
| Single leg Deadlift | Balance and coordination | Improve unilateral strength and balance, prevent muscle imbalance | 8 to 10 reps per leg, 2 to 3 times per week. |
| Romanian Deadlift | Overall hamstring strength | Increases in hamstring and lower back strength reduce injury risk during heavy activities. | 7 to 10 reps, 2 to 3 times per week |
| Glutes Ham Raise | full range of motion strength | Strengthen the hamstring through full ROM and prevent tears and over-extension. | 6 to 8 reps. 2-3 times per week |
Managing Fatigue and Recovery: How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries:
Fatigue contributes to hamstring injuries, especially during the stages of a game or training session. To prevent injury, managing both acute and cumulative fatigue is necessary.
Periodization And Load Management:
Periodization involves structuring training programs to balance workloads and recovery by managing training loads and avoiding sudden increases in intensity. You can prevent the accumulation of fatigue that often leads to injury.
Movement Quality And Assessment:
High-quality movement patterns are the foundation of injury prevention.
How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries By Avoid Over-Stretching:
When flexibility is crucial, stretching the hamstring increases the risk of injury. Despite excessive static stretching, focus on mobility exercises that enhance functional flexibility and muscle strength.
Dynamic Stretching:
Incorporate dynamic stretching into warm-up routines as it improves muscle history without the drawback of static stretching. Exercises like leg swings and walking can reduce hamstring flexibility while preparing the muscles for activity.
How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries By Controlled Mobility Work:
Controlled mobility exercises like yoga and pilates improve overall flexibility and ensure that hamstrings are solid and reliant. These practices emphasize balance coordination and control movements essential for injury prevention.
How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries With These Effective Techniques:
Isometric Hamstring Flex:
To perform an isometric hamstring flex, you must sit on the ground by extending your legs straight in front. Then, raise your knees slightly at a comfortable angle, just around 30 degrees. From the toss of the injured toward the face, hold for 5 seconds. Then relax almost for 7 seconds and then repeat.
Donkey Kickbacks:
To perform this, get down on the knees and hands by bracing the body with palms under the chest, then slowly lift and extend the injured leg to the ceiling. Hold for 15 seconds or do the injury to the ground. Repeat 3 to 7 times.
Nordic Hamstring Exercises:
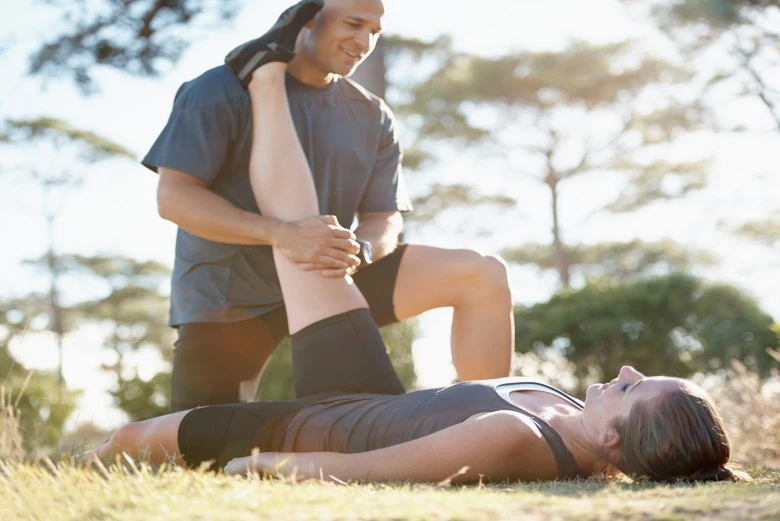
Kneel and ask your partner to reach on both feet to perform this. Slowly lean forward, keeping your legs back and hips aligned. Hold for 10 to 15 seconds, then sit back and repeat.
Single Leg Windmill:
Rest the uninjured leg on a bench or chair by banding the knee. Give the injured leg a straight position by using down toward the toss of the wounded leg. Keep your back flat by holding the stretch for 30 seconds, and repeat it 3 to 7 times. Meanwhile, it is also for the solution to the queries of whether tight hamstrings can cause knee pain and whether tight hamstrings can cause calf pain. You can do that with a leg exercise machine, make sure technique and correct posture matter a lot.
Advanced Exercises with Specific Issues And Their Preventive Benefits:
Know How to prevent hamstring injuries is like having a safety net that keeps you in the game longer. Let’s look at these advanced exercises with specific issues and their preventive benefits.
| Issues | How exercises help | Recommended exercises | Symptoms address | Long term benefits |
| Chronic hamstring tightness | Promote deep muscle stretch, increase flexibility | Romanian deadlift, single Leg Deadlift | Chronic stiffness, Limited mobility | Range of motion, long-term flexibility |
| Recurring hamstrings Strains | Build eccentric strength | Nordic hamstring curl, glute ham raise | Frequent strains, muscle tears | Stronger, more resilient on hamstring |
| Low explosive power | Enhances explosive strength and speed. | Kettlebell swing, sprinter longies. | Poor acceleration reduced athletic performance. | Increased speed and power, improved athletic capabilities. |
| Poor Hip Mobility | Improves his movement and overall mobility. | Romanian deadlift, Single-leg deadlift. | Hip stiffness, a reduced range of motion. | Better functional movement, injury prevention |
| Imbalance in leg strength | Correct muscle imbalances, improve unilateral strength | Pistol squat, single-leg deadlift | Weakness in one leg, instability | Balanced leg strength, improved performance |
| Lack of core stability | Engage more muscle, improve overall stability | Kettlebell swing, single-leg deadlift | poor balance, frequent Falls | A stronger core enhances stability. |
| Knee instability | Strengthen Sporting muscle around the knee, enhance joint stability | Glute – Hum raise, pistol squat | Knee discomfort, instability | Improved knee function, reduced injury risk |
Diagnosis Of Hamstring Injuries: How To Prevent Hamstring Injuries:
Health Care providers can diagnose hamstring injuries based on symptoms data patients reported. They can test tenderness and examine swelling in the hamstring. Sometimes, they can also perform Magnetic resonance imaging tests or MRI.
They can also diagnose a severe injury, discuss how to treat it, and let the patient know where they can return to normal activities. If a patient needs exceptional help, they might also refer them to a physiotherapist, sports medicine specialist, or orthopedic Healthcare provider.
Management And Treatment Of Hamstring Injuries:
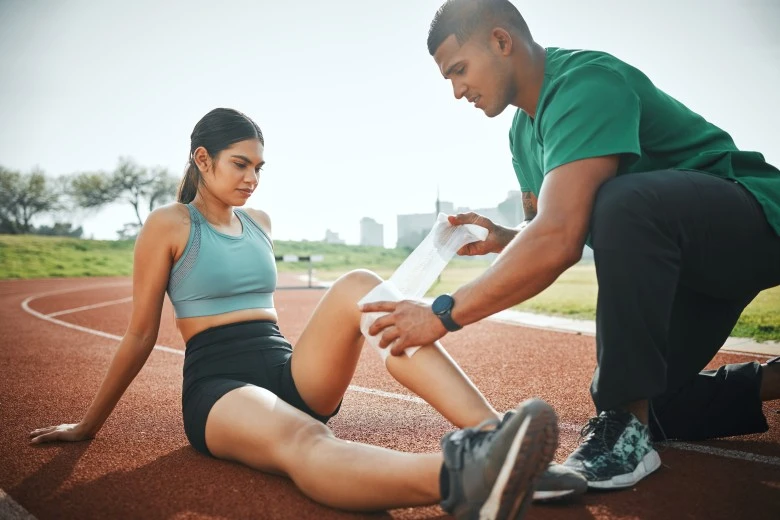

- It is treated at home, but some people need physical therapy. Listen to healthcare providers’ instructions, and try home remedies.
- RICE method followed
- Stop at least two activities until you recover.
- Ice in the area about 20 to 24 hours after injury.
- Keep ice on for 15 minutes, and repeat the process after 13 minutes.
- Use a compression wrap or elastic thigh sleeves.
- Sit on a table with the injured leg hanging off. Gently raise and lower the leg during icing.
- After icing, lie in a prone position on the stomach, gently bandage, and straighten your leg.
Tips For How to Prevent Hamstring Injuries:
Nordic Hamstring Curl:
This is one of the best exercises that target the strength of hamstring muscles. It is the most researched rehabilitation exercise over the past ten years, and much research has shown that this exercise reduces injury rates by 80%. It works eccentrically, which means the muscle works hard (contracting) while lengthening (stretching).
Wearing appropriate footwear is a critical element in preventing hamstring injuries. Eccentric training is also one of the weak points when injuries often occur. The hamstring curl may be the Holy Grail of hamstring entry. Any exercise program should include holistic strength exercises for the lower lamp, pelvis, and back.
Increase Back Mobility:
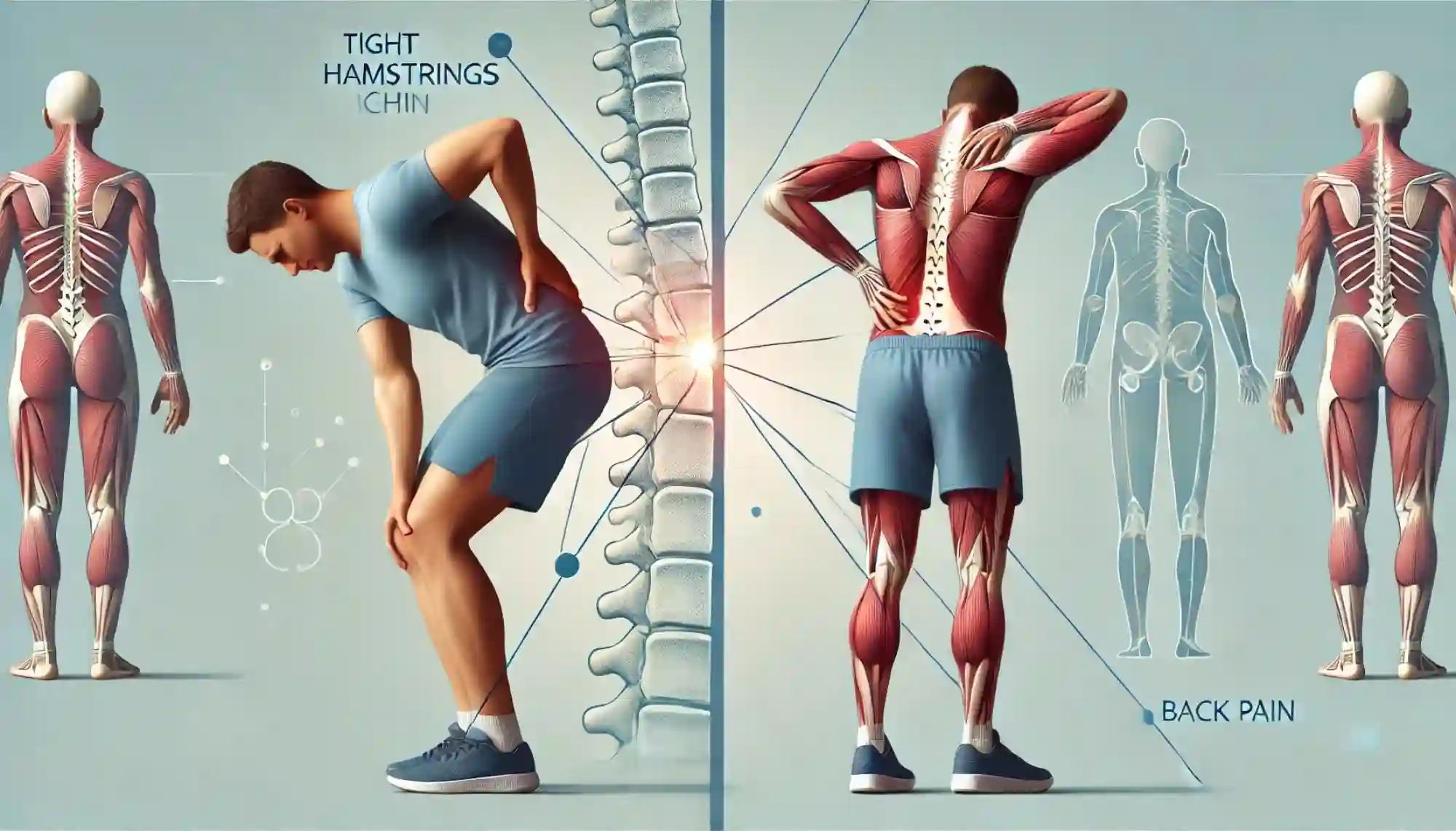
The lower back is where the nerves control the hamstring come from. Many people who develop hamstring strength have coexisting lower back symptoms or problems. These may be as simple as a sensorption of tiredness in the bag with certain activities or as significant as a burning in the vertebral disc. A well-functioning and flexible lower back allows the hamstring to work correctly.
Poor posture at work or sitting at a dash for longer. Of time effects of mobility of back. The hamstring muscles work together with the intern work together with back muscles. Given that these muscles depend on one another for the average and proper functioning of the human body, it makes sense that a healthy lower back is essential for good hamstring performance. If some suffer from back problems, see a physiotherapist for more specific treatment at exercises for advice on posture.
Give Your Body Time To Recover:
Some muscles are more likely to strain when they are fatigued. Fatigue can be expected during a training session, but it can be commutative when the muscular system is used for several weeks due to the training exercises. To counter this, it is suggested that the body be given the best environment for healing and adapting to exercises.
Simple recovery strategies include cold water, good nutrition, swimming in a pool, or some work. Regular messages are also essential to recovery and help fight muscle fatigue while maintaining health issues.
Get Your Nerves Gliding Freely:
A tight back and glutes affect the mobility or flexibility of the nervous system. Nerves can move and bend with the body. Neural tension feels like stiffness down the back of the legs and also leads to misfiring of the hamstring, which puts one at risk of injury. It is better like a misfiring cylinder in a car. The solution is to keep the lower back and glutes healthy, moving properly with specific nerve stretches.
Release the Glutes:
If somebody is training hard in precision build-up or wants to increase activity load, tide glutes are after a consequence. Now, it is not a compliment, and intensity and workload increase the muscles around if they develop notes. This causes pain in the hamstring, reduces flexibility, and increases the risk of training the muscles, as glutes and hamstrings are vital working partners. A regular deep-tissue massage by a therapist may be a feature to maintain loose glutes and release Trigger points.
Impact of Tight Hamstrings on Other Body Parts

In addition to focusing on preventing hamstring injuries, it’s important to consider how tight hamstrings can affect other areas of the body. For instance, can tight hamstrings cause knee pain? Yes, they can, as the tension in the hamstrings may lead to increased stress on the knees. Additionally, can tight hamstrings cause back pain? Absolutely. The interconnectedness of the hamstrings and lower back means that tightness in these muscles can contribute to discomfort and pain in the back. Addressing these issues holistically can be key to maintaining overall body health.
Conclusion:
Someone with a hamstring injury must be concerned about treatment and advice. If somebody suffers from hamstring strain at any point, he should apply the RICE method of rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Make an appointment with a clinic practitioner, Physiotherapist, orthotic, and zero-factor to immediately move in the right direction and eliminate the pain. If you still have some questions, ask in the comment below.

Ahmad Hassan is a fitness writer and transformation coach behind GymWithMind.com, specializing in the Skinny to Muscular Transformation niche. After going from 51 kg to 65 kg naturally, he now shares science-backed, practical strategies to help skinny guys build lean muscle through smart training, balanced nutrition, and consistency. His guides blend real experience with research to make fitness simple, achievable, and sustainable

 Skinny to Muscular1 year ago
Skinny to Muscular1 year agoRealistic 6 Month Body Transformation Female: From Struggle To Power
 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years agoDiscover Elite Body Sculpting: Best 8 Method Revealed For Precision Shaping:

 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years agoBody Fitness Tips For Female; Unleashing Fitness Secrets

 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years agoHow To Lose 50 Pounds in 5 Months: Is it possible ?

 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years ago9 Best Front Squat Alternative At Home And Gym:

 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years ago15 Best Strength And Conditioning Books

 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years agoTop 12 Books For Strength Coaches:

 Skinny to Muscular2 years ago
Skinny to Muscular2 years agoKettlebell Golf Workout;- Get Ready For Swing
